|
|
|
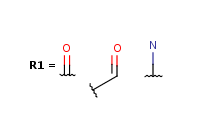 |
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
chemaxon.struc.RgMolecule
class.
MolAtom.RGROUP constant in
the constructor of the MolAtom. Using the MolAtom.setRgroup(int),
an ID can be set for the R-atom.
MolAtom r1 = new MolAtom(MolAtom.RGROUP); r1.setRgroup(1);Note, that R-atoms are MolAtom objects, hence they should be added to the root molecule.
RgMolecule.setRoot(MoleculeGraph)
method.
RgMolecule rgMol = new RgMolecule(); rgMol.setRoot(root);
Molecule objects.
To define an R-group attachment point to one of its atoms use the
MolAtom.addRgroupAttachmentPoint(int, int).
With the first integer the order of the attachment point is set, the second
one defines the bond type.
R-group definition should be added to the corresponding R-group using the
Rgmolecule.addRgroup(int, Molecule). The integer parameter
shows to which R-atom the definition corresponds to.
Molecule rg = MolImporter.importMol("O");
rg.getAtom(0).addRgroupAttachmentPoint(1, 1);
rgMol.addRgroup(1, rg);
You may find a full example here.
//get the root structure and enumerate the atoms, find R-Atoms.
Molecule root = rgmol.getRoot();
for (int i = root.getAtomCount() - 1; i >= 0; --i){
MolAtom atom = root.getAtom(i);
if (atom.getAtno() == MolAtom.RGROUP){
....
}
}
//enumerate the R-group definitions and its fragments
int nr = rgmol.getRgroupCount();
for(int i = 0; i < nr; ++i) {
int nrm = rgmol.getRgroupMemberCount(i);
for(int j = 0; j < nrm; ++j) {
// .... do something with rgmol.getRgroupMember(i, j)
}
}
|
Previous chapter |
Next chapter |